Inbalance grid: smart EV charging solution
The solution allows installing charging stations in locations with limited power and scaling despite grid limitations. Reducing costs, increasing profitability and entering challenging locations.
Supported by: EIT Urban Mobility
Product Details
Having identified grid limitation as the major bottleneck for charging infrastructure development, the company has created and innovated a solution from the ground up to be ready for mass EV adoption.
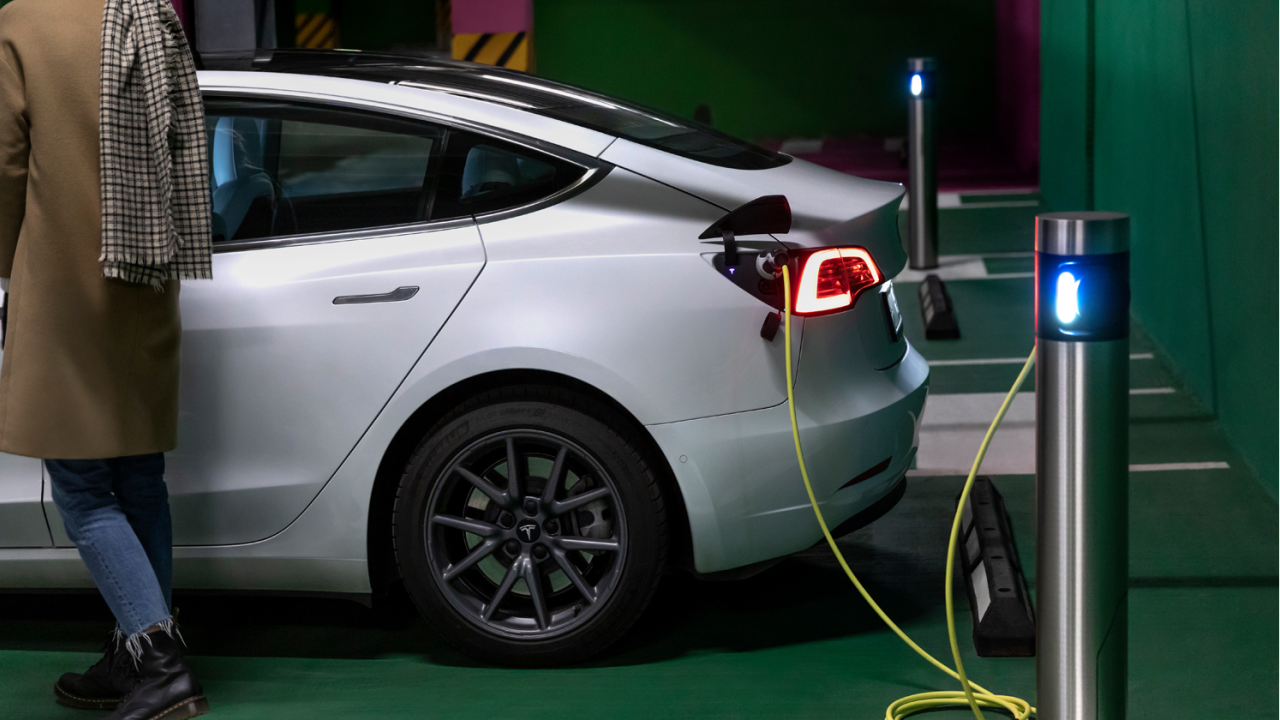
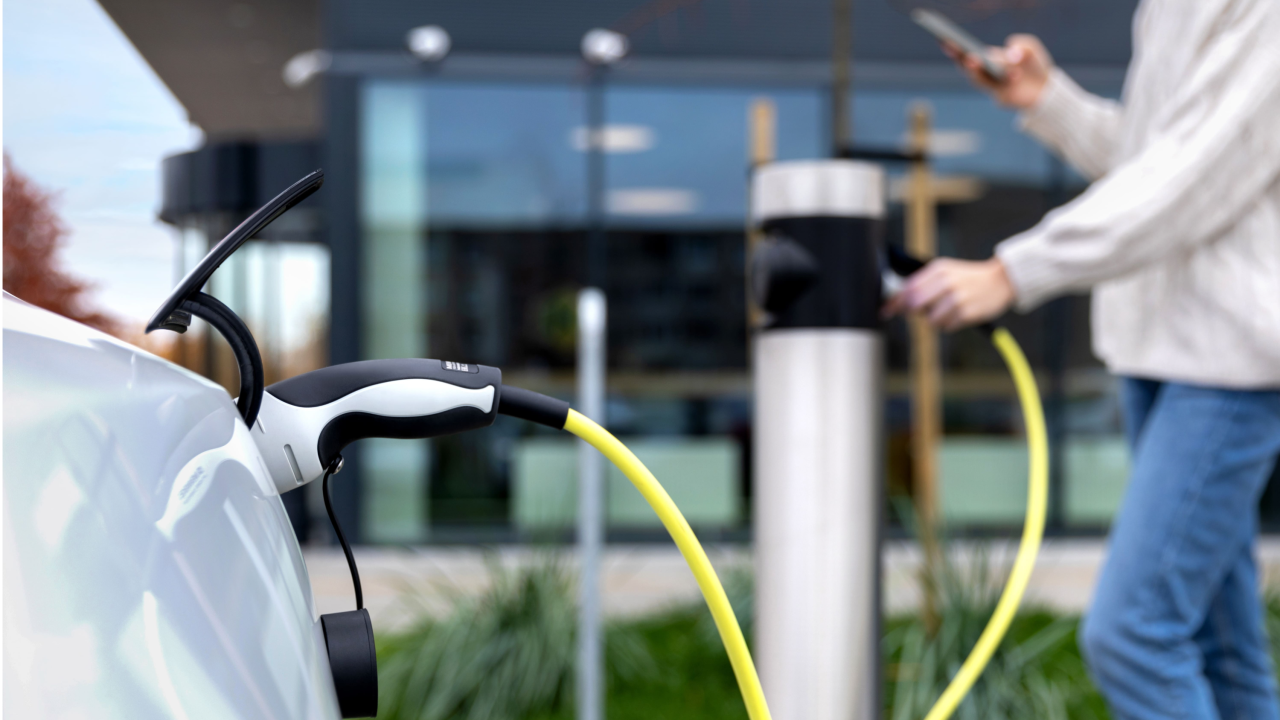
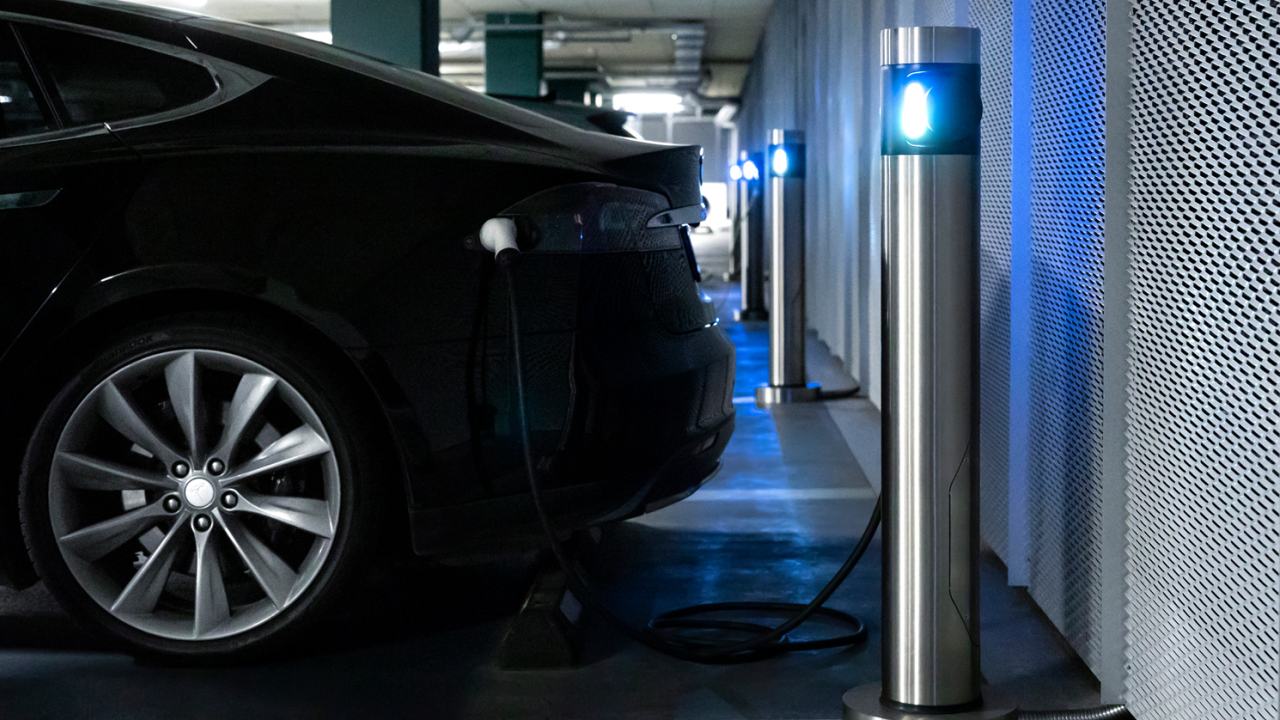
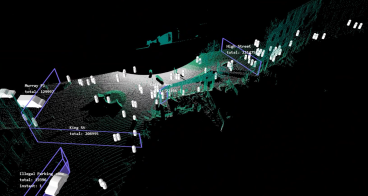
Inbalance Grid is overcoming this barrier via a cloud-based, AI-powered dynamic load management technology, which allows to build more charging points with less dedicated power, avoiding unsustainable and expensive grid upgrades.
The solution is cloud & software-based and is not limited to wiring and/or physical equipment. The cloud-controlled charger network can fill up EVs only by taking the non-used power from the buildings or the grid itself. And distribute that available power to multiple charging points so that each vehicle is charged at optimal speed. Such innovative installations have various effects on a building’s sustainability, extend grid capacity, and drastically reduce CAPEX needed for EV charging infrastructure.
Availability
Discover cities and markets where the product is available